Optimixation is a new term describing the unintended negative consequences that occur when optimization is taken too far. OPTIMIXATION refers to the practice of selecting and combining elements from various methods in the hope that the resulting mix will produce a superior management approach. While this might seem like a smart strategy, it often stems […]
Blog
Meetup CIO25
The Meetup CIO 25 – AI Implications to IT Management was successfully completed, bringing together IT leaders to explore the strategic and operational impacts of AI on modern IT management. The session featured insightful discussions on AI-driven governance, evolving roles of IT teams, and practical approaches to integrating intelligent agents into daily operations. Participants shared […]
Continually Improving the Wrong Thing
…such as the customer experience of fixing broken IT systems. The service industry evolved long ago, around the time when innovative services began targeting top-tier clients willing to pay premium prices—think airlines, banking, and hotels. In those sectors, delighting customers by delivering an outstanding experience was a legitimate strategy: it helped grow the market, improve […]
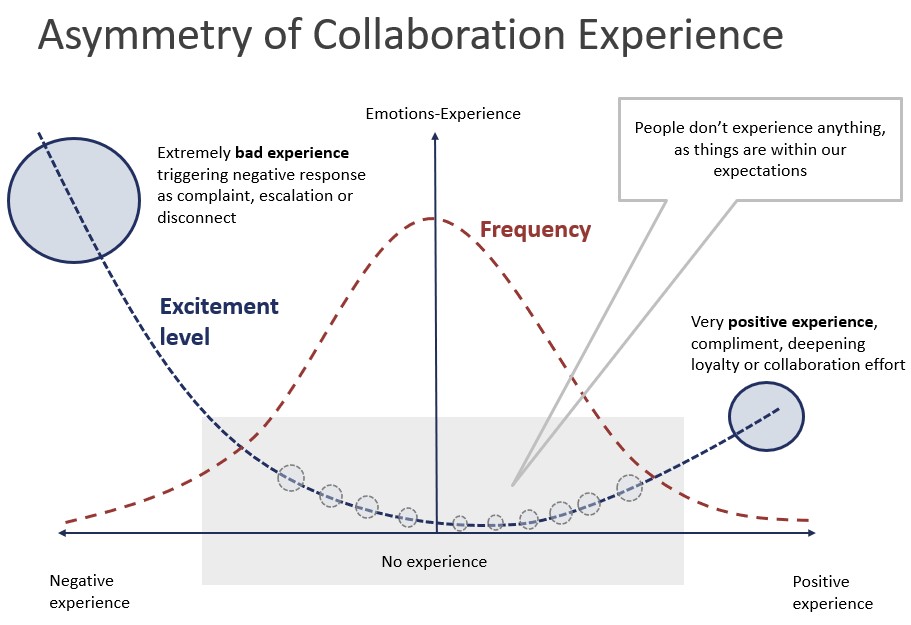
When Feedback Becomes a Mispractice
The habit of collecting feedback after every interaction has become a widespread mispractice—driven by the uncritical adoption of customer-oriented management models beyond their original scope. Slogans like “The customer is king” or “We are here to serve you” reflect underlying mental models that are being applied in contexts fundamentally different from the transactional relationships for […]
The 12 Outdated Assumptions Still Used in IT Management
Colleagues Prefer to Be Treated as Customers Collaboration is often mistaken for a service relationship. Unlike transactions, collaboration is non-transactional and requires a fundamentally different approach. Demand Is Endless The belief that working faster and more efficiently will meet endless demand overlooks what truly matters: delivering meaningful outcomes. Quality and relevance outweigh speed and volume. […]